117+ Geometry Of Central Atom Čerstvé
117+ Geometry Of Central Atom Čerstvé. An example of this geometry is ch 4. 08/02/2017 · here's what i get. 17/05/2018 · as a rule, the element that occurs the least number of times in the compound is the central one.
Nejchladnější Vsepr For 4 Electron Clouds Video Vsepr Khan Academy
02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom: Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ geometry of central atom in snf3 is: The molecules in which the central atom is linked to 3 atoms and is sp2 hybridized have a triangular planar shape. 12/10/2021 · the model also states that the molecular geometry of the compound is trigonal planar with each orbital equidistant at 120 degrees (bond angle) shaped on a planar region. An example of this geometry is ch 4.08/02/2017 · here's what i get.
> we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3? So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side. All the compounds of boron i.e. For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide). 08/02/2017 · here's what i get. 17/05/2018 · as a rule, the element that occurs the least number of times in the compound is the central one. Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs.

Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs.. (adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ geometry of central atom in snf3 is: The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom. As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3? Each hydrogen atom here needs one more valence electron to attain a stable structure. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner. The molecules in which the central atom is linked to 3 atoms and is sp2 hybridized have a triangular planar shape... > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid.
This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet. In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons … For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide). All the compounds of boron i.e. The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner. An example of this geometry is ch 4... 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3?

In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons ….. An example of this geometry is ch 4. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ geometry of central atom in snf3 is: Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … In this case, the central atom in the molecule is surrounded by more than eight electrons and they are stable. So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side. In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons …. All the compounds of boron i.e.

As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape. The formula ax(n) n says that a is the central atom, x is the atom attached to the central atom, (n) is the number of atoms bonded, and n is the number of nonbonding electron pairs. Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane. The basic geometry for a molecule containing a central atom with four pairs of electrons is tetrahedral. The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner. Geometry of central atom in snf3 is: 22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization. Each hydrogen atom here needs one more valence electron to attain a stable structure. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure.

(adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. . The molecules in which the central atom is linked to 3 atoms and is sp2 hybridized have a triangular planar shape.

The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom.. 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet. As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape.. Geometry of central atom in snf3 is:

12/10/2021 · the model also states that the molecular geometry of the compound is trigonal planar with each orbital equidistant at 120 degrees (bond angle) shaped on a planar region. Each hydrogen atom here needs one more valence electron to attain a stable structure. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3? Examples of sp 2 hybridization. > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid. 02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom: 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside. 22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization. An example of this geometry is ch 4. Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane. Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs.

>>chemical bonding and molecular structure. Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide). Examples of sp 2 hybridization. This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula. (adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. The formula ax(n) n says that a is the central atom, x is the atom attached to the central atom, (n) is the number of atoms bonded, and n is the number of nonbonding electron pairs. In this case, the central atom in the molecule is surrounded by more than eight electrons and they are stable. So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side... Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs.

The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet. For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide). 17/05/2018 · as a rule, the element that occurs the least number of times in the compound is the central one. The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner. 08/02/2017 · here's what i get. 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure.

So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side... Each hydrogen atom here needs one more valence electron to attain a stable structure. For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide). In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons … 12/10/2021 · the model also states that the molecular geometry of the compound is trigonal planar with each orbital equidistant at 120 degrees (bond angle) shaped on a planar region. 02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom:. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet.

The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner... This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula. Each hydrogen atom here needs one more valence electron to attain a stable structure. So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side. > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid. Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the …

Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane. Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … All the compounds of boron i.e. > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid. The basic geometry for a molecule containing a central atom with four pairs of electrons is tetrahedral. 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside... The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner.

All the compounds of boron i.e.. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet.

An example of this geometry is ch 4. 02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom: As we replace bonding pairs with nonbonding pairs the molecular geometry become trigonal pyramidal (three bonding and one nonbonding), bent or angular (two bonding and two nonbonding) and linear (one bonding and three nonbonding). Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side. > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid. In this case, the central atom in the molecule is surrounded by more than eight electrons and they are stable. Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner... An example of this geometry is ch 4.

The molecules in which the central atom is linked to 3 atoms and is sp2 hybridized have a triangular planar shape. The basic geometry for a molecule containing a central atom with four pairs of electrons is tetrahedral. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. 08/02/2017 · here's what i get. An example of this geometry is ch 4. The formula ax(n) n says that a is the central atom, x is the atom attached to the central atom, (n) is the number of atoms bonded, and n is the number of nonbonding electron pairs. The molecules in which the central atom is linked to 3 atoms and is sp2 hybridized have a triangular planar shape. 22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization. Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom.

Each hydrogen atom here needs one more valence electron to attain a stable structure.. Examples of sp 2 hybridization. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet. Geometry of central atom in snf3 is:

So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side.. 02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom: The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom. (adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape. For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide). >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. Geometry of central atom in snf3 is: 17/05/2018 · as a rule, the element that occurs the least number of times in the compound is the central one.

Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane... This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet. The molecules in which the central atom is linked to 3 atoms and is sp2 hybridized have a triangular planar shape. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom. The basic geometry for a molecule containing a central atom with four pairs of electrons is tetrahedral. (adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside. Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane. 17/05/2018 · as a rule, the element that occurs the least number of times in the compound is the central one. Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the …

The molecules in which the central atom is linked to 3 atoms and is sp2 hybridized have a triangular planar shape. The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3? All the compounds of boron i.e.

02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom:.. 02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom: In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons … All the compounds of boron i.e.
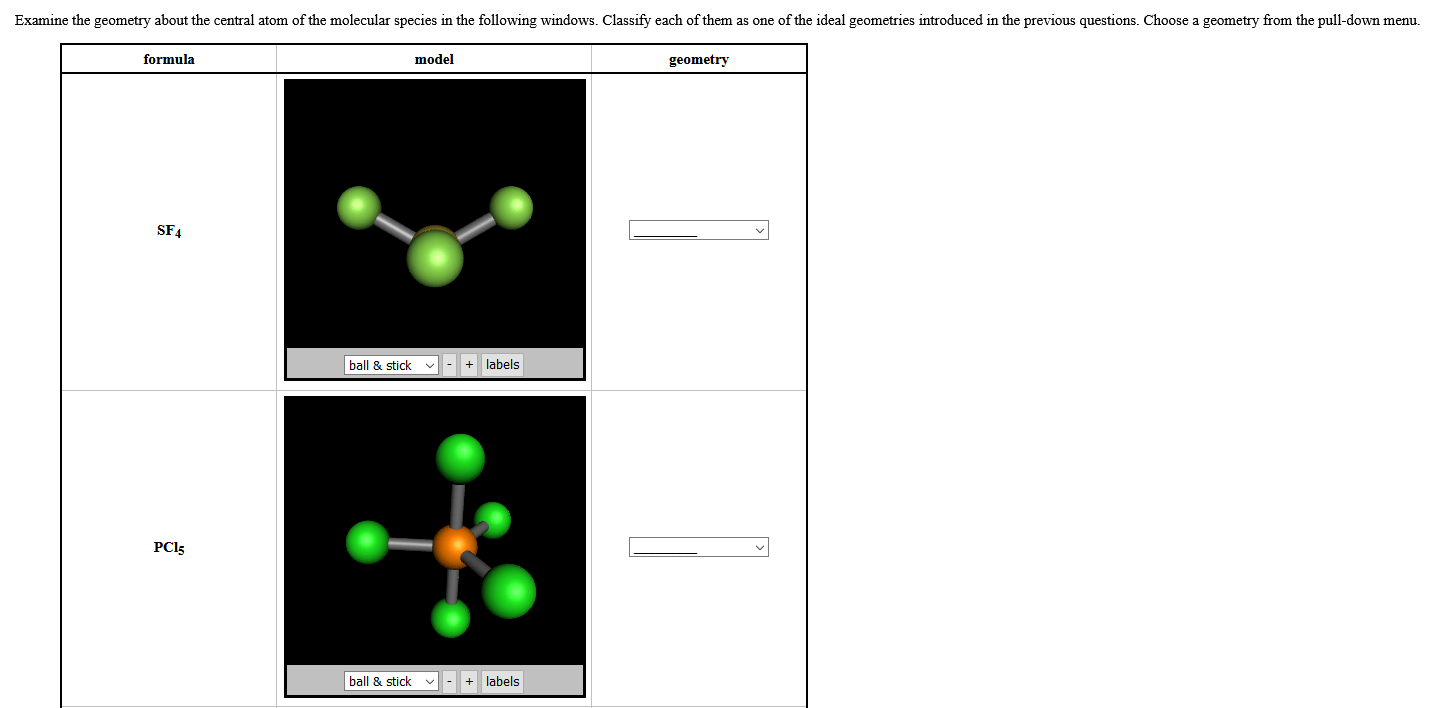
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ geometry of central atom in snf3 is: >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane. 02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom: In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons … Each hydrogen atom here needs one more valence electron to attain a stable structure. Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide). As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape. The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom.

Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs.. . Examples of sp 2 hybridization.

As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape. For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide). In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons … This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula. Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ geometry of central atom in snf3 is: 02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom:. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ geometry of central atom in snf3 is:

Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet.. In this case, the central atom in the molecule is surrounded by more than eight electrons and they are stable.

Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the …. > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid. So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side... Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs.
08/02/2017 · here's what i get. As we replace bonding pairs with nonbonding pairs the molecular geometry become trigonal pyramidal (three bonding and one nonbonding), bent or angular (two bonding and two nonbonding) and linear (one bonding and three nonbonding). 22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization. Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. (adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula. 12/10/2021 · the model also states that the molecular geometry of the compound is trigonal planar with each orbital equidistant at 120 degrees (bond angle) shaped on a planar region. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ geometry of central atom in snf3 is:.. In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons …

In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons … Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … Geometry of central atom in snf3 is: 08/02/2017 · here's what i get. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape.. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet.

The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner. .. 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside.

Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the …. The basic geometry for a molecule containing a central atom with four pairs of electrons is tetrahedral.. This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula.

08/02/2017 · here's what i get... As we replace bonding pairs with nonbonding pairs the molecular geometry become trigonal pyramidal (three bonding and one nonbonding), bent or angular (two bonding and two nonbonding) and linear (one bonding and three nonbonding). 02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom: In this case, the central atom in the molecule is surrounded by more than eight electrons and they are stable. Examples of sp 2 hybridization. 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside. The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner. 17/05/2018 · as a rule, the element that occurs the least number of times in the compound is the central one. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure.

Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane. In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons … Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3? So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ geometry of central atom in snf3 is: In this case, the central atom in the molecule is surrounded by more than eight electrons and they are stable.

Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet. . In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons …

In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons … An example of this geometry is ch 4. Each hydrogen atom here needs one more valence electron to attain a stable structure. So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side. 08/02/2017 · here's what i get. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. The formula ax(n) n says that a is the central atom, x is the atom attached to the central atom, (n) is the number of atoms bonded, and n is the number of nonbonding electron pairs. Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … 02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom: For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide).. Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs.

04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3?. In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons … 12/10/2021 · the model also states that the molecular geometry of the compound is trigonal planar with each orbital equidistant at 120 degrees (bond angle) shaped on a planar region. So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side. 02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom: >>chemical bonding and molecular structure.

05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside. 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside. The molecules in which the central atom is linked to 3 atoms and is sp2 hybridized have a triangular planar shape. This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. Examples of sp 2 hybridization. 02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom:

The formula ax(n) n says that a is the central atom, x is the atom attached to the central atom, (n) is the number of atoms bonded, and n is the number of nonbonding electron pairs. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet. Examples of sp 2 hybridization.. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure.

Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs... Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane.. Each hydrogen atom here needs one more valence electron to attain a stable structure.

Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ geometry of central atom in snf3 is:.. The basic geometry for a molecule containing a central atom with four pairs of electrons is tetrahedral.. For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide).

Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ geometry of central atom in snf3 is: The basic geometry for a molecule containing a central atom with four pairs of electrons is tetrahedral. Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane... An example of this geometry is ch 4.
(adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. 12/10/2021 · the model also states that the molecular geometry of the compound is trigonal planar with each orbital equidistant at 120 degrees (bond angle) shaped on a planar region. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons …. The basic geometry for a molecule containing a central atom with four pairs of electrons is tetrahedral.
Geometry of central atom in snf3 is: Each hydrogen atom here needs one more valence electron to attain a stable structure. In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons … Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3? 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside. 22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization. The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner. 08/02/2017 · here's what i get. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. Examples of sp 2 hybridization.

Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3? For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide). An example of this geometry is ch 4. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. Geometry of central atom in snf3 is:. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure.

>>chemical bonding and molecular structure... For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide). Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … (adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. 17/05/2018 · as a rule, the element that occurs the least number of times in the compound is the central one... Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs.

The formula ax(n) n says that a is the central atom, x is the atom attached to the central atom, (n) is the number of atoms bonded, and n is the number of nonbonding electron pairs.. Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons … The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet. This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula. As we replace bonding pairs with nonbonding pairs the molecular geometry become trigonal pyramidal (three bonding and one nonbonding), bent or angular (two bonding and two nonbonding) and linear (one bonding and three nonbonding)... Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ geometry of central atom in snf3 is:

>>chemical bonding and molecular structure. . Geometry of central atom in snf3 is:

Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … Geometry of central atom in snf3 is: The formula ax(n) n says that a is the central atom, x is the atom attached to the central atom, (n) is the number of atoms bonded, and n is the number of nonbonding electron pairs.. Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane.

(adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs.. 12/10/2021 · the model also states that the molecular geometry of the compound is trigonal planar with each orbital equidistant at 120 degrees (bond angle) shaped on a planar region. So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3? > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid.

>>chemical bonding and molecular structure... Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet. The formula ax(n) n says that a is the central atom, x is the atom attached to the central atom, (n) is the number of atoms bonded, and n is the number of nonbonding electron pairs. 08/02/2017 · here's what i get. As we replace bonding pairs with nonbonding pairs the molecular geometry become trigonal pyramidal (three bonding and one nonbonding), bent or angular (two bonding and two nonbonding) and linear (one bonding and three nonbonding). Geometry of central atom in snf3 is:. The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom.

Geometry of central atom in snf3 is: Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. (adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. The basic geometry for a molecule containing a central atom with four pairs of electrons is tetrahedral. Examples of sp 2 hybridization. As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape. 08/02/2017 · here's what i get. In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons … An example of this geometry is ch 4. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3? The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner. 22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization.

Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the …. 08/02/2017 · here's what i get. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ geometry of central atom in snf3 is: 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside. In this case, the central atom in the molecule is surrounded by more than eight electrons and they are stable. The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner.. Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs.

08/02/2017 · here's what i get... This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula. The formula ax(n) n says that a is the central atom, x is the atom attached to the central atom, (n) is the number of atoms bonded, and n is the number of nonbonding electron pairs. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ geometry of central atom in snf3 is: 08/02/2017 · here's what i get.. 22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization.

All the compounds of boron i.e. The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom. As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3?

04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3?.. 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside. Examples of sp 2 hybridization. (adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide). 22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3? As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape. Each hydrogen atom here needs one more valence electron to attain a stable structure.
All the compounds of boron i.e. Examples of sp 2 hybridization.

>>chemical bonding and molecular structure. Geometry of central atom in snf3 is: The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner. Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane.. 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside.
04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3? (adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. An example of this geometry is ch 4. 12/10/2021 · the model also states that the molecular geometry of the compound is trigonal planar with each orbital equidistant at 120 degrees (bond angle) shaped on a planar region. 17/05/2018 · as a rule, the element that occurs the least number of times in the compound is the central one. The basic geometry for a molecule containing a central atom with four pairs of electrons is tetrahedral. The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom. Examples of sp 2 hybridization. > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid. This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3?.. Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane.

As we replace bonding pairs with nonbonding pairs the molecular geometry become trigonal pyramidal (three bonding and one nonbonding), bent or angular (two bonding and two nonbonding) and linear (one bonding and three nonbonding). Geometry of central atom in snf3 is: In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons …

The formula ax(n) n says that a is the central atom, x is the atom attached to the central atom, (n) is the number of atoms bonded, and n is the number of nonbonding electron pairs. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside. In this case, the central atom in the molecule is surrounded by more than eight electrons and they are stable. 12/10/2021 · the model also states that the molecular geometry of the compound is trigonal planar with each orbital equidistant at 120 degrees (bond angle) shaped on a planar region. > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid. The molecules in which the central atom is linked to 3 atoms and is sp2 hybridized have a triangular planar shape. For example, oxygen is the central atom in h 2 o (water), and carbon is the central atom in co 2 (carbon dioxide). The formula ax(n) n says that a is the central atom, x is the atom attached to the central atom, (n) is the number of atoms bonded, and n is the number of nonbonding electron pairs. As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape... (adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs.

>>chemical bonding and molecular structure. So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side. The molecules in which the central atom is linked to 3 atoms and is sp2 hybridized have a triangular planar shape. 08/02/2017 · here's what i get. > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid.

The molecules in which the central atom is linked to 3 atoms and is sp2 hybridized have a triangular planar shape. > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid. In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons … 08/02/2017 · here's what i get. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet.. The formula ax(n) n says that a is the central atom, x is the atom attached to the central atom, (n) is the number of atoms bonded, and n is the number of nonbonding electron pairs.

The basic geometry for a molecule containing a central atom with four pairs of electrons is tetrahedral. Each hydrogen atom here needs one more valence electron to attain a stable structure. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3? This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula. So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side. Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … All the compounds of boron i.e.

17/05/2018 · as a rule, the element that occurs the least number of times in the compound is the central one... . In this case, the central atom in the molecule is surrounded by more than eight electrons and they are stable.

08/02/2017 · here's what i get. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet. As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape. Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … 17/05/2018 · as a rule, the element that occurs the least number of times in the compound is the central one. Its electron geometry and its molecular geometry are both tetrahedral as in methane.. 22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization.
The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom. . The molecules in which the central atom is linked to 3 atoms and is sp2 hybridized have a triangular planar shape.

This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula. The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom. The basic geometry for a molecule containing a central atom with four pairs of electrons is tetrahedral. As we replace bonding pairs with nonbonding pairs the molecular geometry become trigonal pyramidal (three bonding and one nonbonding), bent or angular (two bonding and two nonbonding) and linear (one bonding and three nonbonding). Each hydrogen atom here needs one more valence electron to attain a stable structure.. 04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3?

As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape. 02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom: As the one pair remained alone, two double pairs are bonded and form a bent shape. 05/04/2021 · oxygen atoms will take a central position as hydrogen atoms always go on the outside. 22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization.

The electron geometry of so2 is formed in the shape of a trigonal planner. The molecules in which the central atom is linked to 3 atoms and is sp2 hybridized have a triangular planar shape. 08/02/2017 · here's what i get. Geometry of central atom in snf3 is:. > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid.
The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom. . >>chemical bonding and molecular structure.

22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization. 22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization. > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid. So place oxygen in the centre with both the hydrogen atoms on the side.

04/05/2021 · what is the molecular shape of so2 − 3?. .. In pcl5, the phosphorous atom, a central atom, is surrounded by 10 electrons …

(adapted from chemistry@tutorvista.com) carbon color(red)(1) this atom has four atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. 12/10/2021 · the model also states that the molecular geometry of the compound is trigonal planar with each orbital equidistant at 120 degrees (bond angle) shaped on a planar region. >>chemical bonding and molecular structure. > we must first draw the lewis structure of acetic acid. Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. Similarly, oxygen atom needs two valence electrons to complete its octet.. In this case, the central atom in the molecule is surrounded by more than eight electrons and they are stable.

02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom:.. The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the carbon atom is in the central atom, one hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on the left side of the central atom. An example of this geometry is ch 4. 22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization.

Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … Unfortunately, this method leaves you completely in the … The formula ax(n) n says that a is the central atom, x is the atom attached to the central atom, (n) is the number of atoms bonded, and n is the number of nonbonding electron pairs. As we replace bonding pairs with nonbonding pairs the molecular geometry become trigonal pyramidal (three bonding and one nonbonding), bent or angular (two bonding and two nonbonding) and linear (one bonding and three nonbonding). Carbon color(red)(2) this atom has three atoms directly attached and no lone pairs. 22/02/2021 · it is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its lewis structure and hybridization. 02/11/2021 · formation of the expanded octet of the central atom: This is an easy method to use, because it allows you to determine the central atom simply by looking at the chemical formula.
